Fog Computing vs Edge Computing
“Fog Computing vs Edge Computing”, one of the newer battlefields, refers to the confrontation between two hotspots. Dive into the depths of Fog Computing vs Edge Computing and discover their subtle intricacies, practical cases, and future implications for these concepts. Let’s discuss ways in which Fog Computing differs from Edge Computing, unveiling how they influence modern-day computing.
Fog Computing:
On the other hand, Fog computing extends to Cloud Computing Architecture. It is a distributed framework carrying services and resources that have been promoted to the edge of the network. Focusing on the localization of computing power next to the end-users and devices is the guiding principle of this technology. This allows the transmission to users and devices faster and enhances the overall user experience.
Characteristics
- Proximity
- Scalability
- Heterogeneity
Architecture
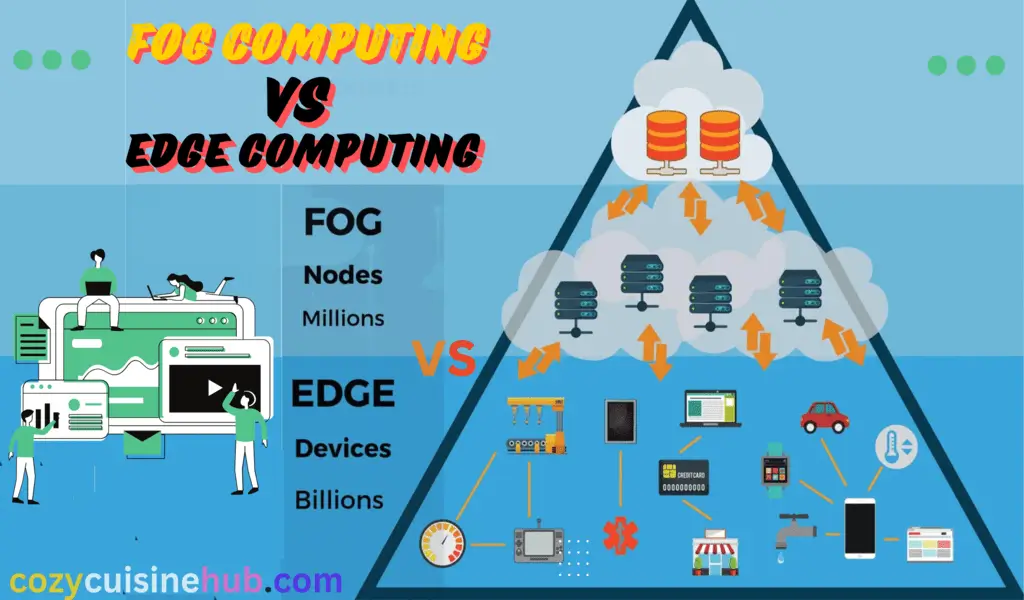
Fog computing model is a network system of fog nodes, gateways and cloud servers that implements the layered approach. Fog nodes are simply fog edge devices that process data and analysis. At the same time, gateways are the links and in order for the cloud and edge devices to communicate.
Edge Computing:
Edge computing involves carrying out information and cognition near the network edge, where there is more data generation. Its main task is the distribution and conservation of latency and bandwidth by carrying out computational tasks and analyses before forwarding only the relevant data to the central cloud system.
Characteristics
- Low Latency
- Distributed Architecture
- Resource Efficiency
Architecture
Edge computing architecture constitutes endpoint devices, edge servers, and cloud infrastructure. IoT nodes like sensors and handheld devices are used to gather data, and edge-edge servers perform local data processing and exploration. Cloud infrastructure provides extra hardware capacity used for doing complex orders like retrieving data.
Future Trends and Applications
The creative verticals of fog computing and edge computing have the capacity to be the change for the future, as the latest technologies bring on innovations in different varieties of the industries. From the process of self-driving cars to the intelligent healthcare systems they will be further progressing day by day and are therefore able to make the manner of data and computational resources human-centered.
“Proximity to End Users“
Fog Computing: Nurting proximity to ultimate users and gadgets, usually deployed at the edge of the network.
Edge Computing: This leads to storing data in the first instance of the network, as if on a device or computer too.
Scalability
Fog Computing: Scalable structure to offer such practices that can be used during workload fluctuations and changing network conditions.
Edge Computing: Utilizes distributed architecture to improve scalability by rendering computational resources from edge devices.
Resource Management
Fog Computing: Operating a centralized algorithmic control management, which commands fog nodes to organize the task of data dealing.
Edge Computing: Distributed resource management that has edge devices automatically completing computing and analysis tasks without any human operation.
Security and Privacy
Fog Computing: The central security system guarantees a universal deployment of data confidential and intact data state at a fog network.
Edge Computing: Puts the focus on local device security and privacy, the data of which is stored and processed at the device level.
“Use Cases of fog and edge computing “
Fog Computing Use Cases
Smart Cities: This technology supports real-time monitoring and governing of urban infrastructure through traffic lights and environmental signals.
Industrial IoT: The fog-computing feature makes it possible for industry settings’ predictive maintenance and optimization of processes based on sensor data analysis to be done locally.
Edge Computing Use Cases
Autonomous Vehicles: Smart cars such as autonomous vehicles are greatly aided by edge computing for real-time operations which delivers decision making locally where the data is generated.
Healthcare: on the edge, there resides remote patient monitoring and that real-time health data analytics which collectively assists in improving healthcare delivery.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Fog Computing |
Low Latency | Complexity |
| Scalability | Dependency on Connectivity | |
| Data Privacy | ||
Edge Computing |
Real-Time Processing | Limited Resources |
| Reduced Bandwidth Usage | Security Concerns |
“Conclusion”
Unlike fog computing, which works on the principle of proximity and centralized management to end users, edge computing on the other hand is about processing of data almost as close to the immediate edge of the network scheme with a distributed architecture. Knowing and using the computing models correctly is imperative for companies and organizations that look to spread innovation and attain higher possibilities for productivity by utilizing the distributed computing power.
FAQs:
How does cloud computing and edge computing vary from one another?
Fog computing highlights the organization’s proximity to users and centralized management systems, while edge computing involves the processing of data at the actual edge of the network with distributed authority.
Why and what industrial applications do we apply to Fog and Edge computing?
Edge computing is indispensable in various cases like autonomous vehicles, the healthcare industry and where data processing demands precise timing.